
The quadriceps femoris consists of four individual muscles - the three vastus muscles and the rectus femoris. Fig 1 - The muscles of the anterior thigh.

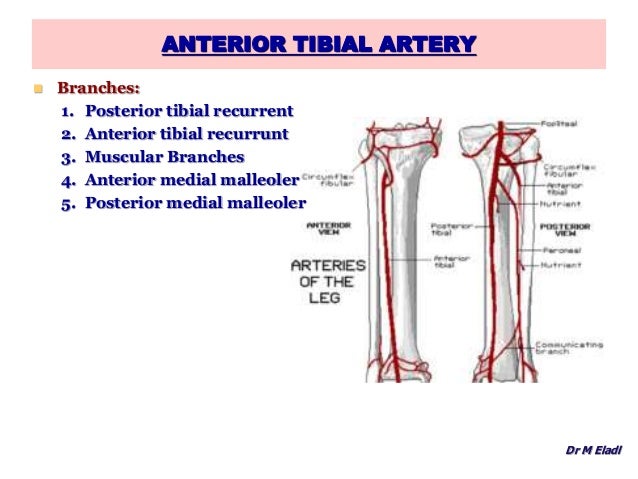
Proximal attachment: Originates from the anterior and lateral surfaces of the femoral shaft.It has a secondary function of stabilising the patella. Proximal attachment: Originates from the greater trochanter and the lateral lip of linea aspera of the femur.The patella, in turn, is attached to the tibial tuberosity by the patella ligament. The four muscles collectively insert onto the patella via the quadriceps tendon. It forms the main bulk of the anterior thigh, and is one of the most powerful muscles in the body. arthroplasty, high tibial osteotomy, lateral meniscal repair, posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction) 4,5.The quadriceps femoris consists of four individual muscles – the three vastus muscles and the rectus femoris. Recognition of high-origin and aberrant anterior tibial arteries is important to reduce the risk of inadvertent vascular injury, during knee surgery (e.g. high-origin anterior tibial artery that courses between the posterior tibial cortex and popliteus.origin above proximal to the popliteus muscle belly.high-origin/high-division anterior tibial artery 4.anterior lateral malleolar artery: anastomoses with the perforating branch of the peroneal artery.anterior medial malleolar artery: anastomoses with the medial malleolar branch of the posterior tibial artery.
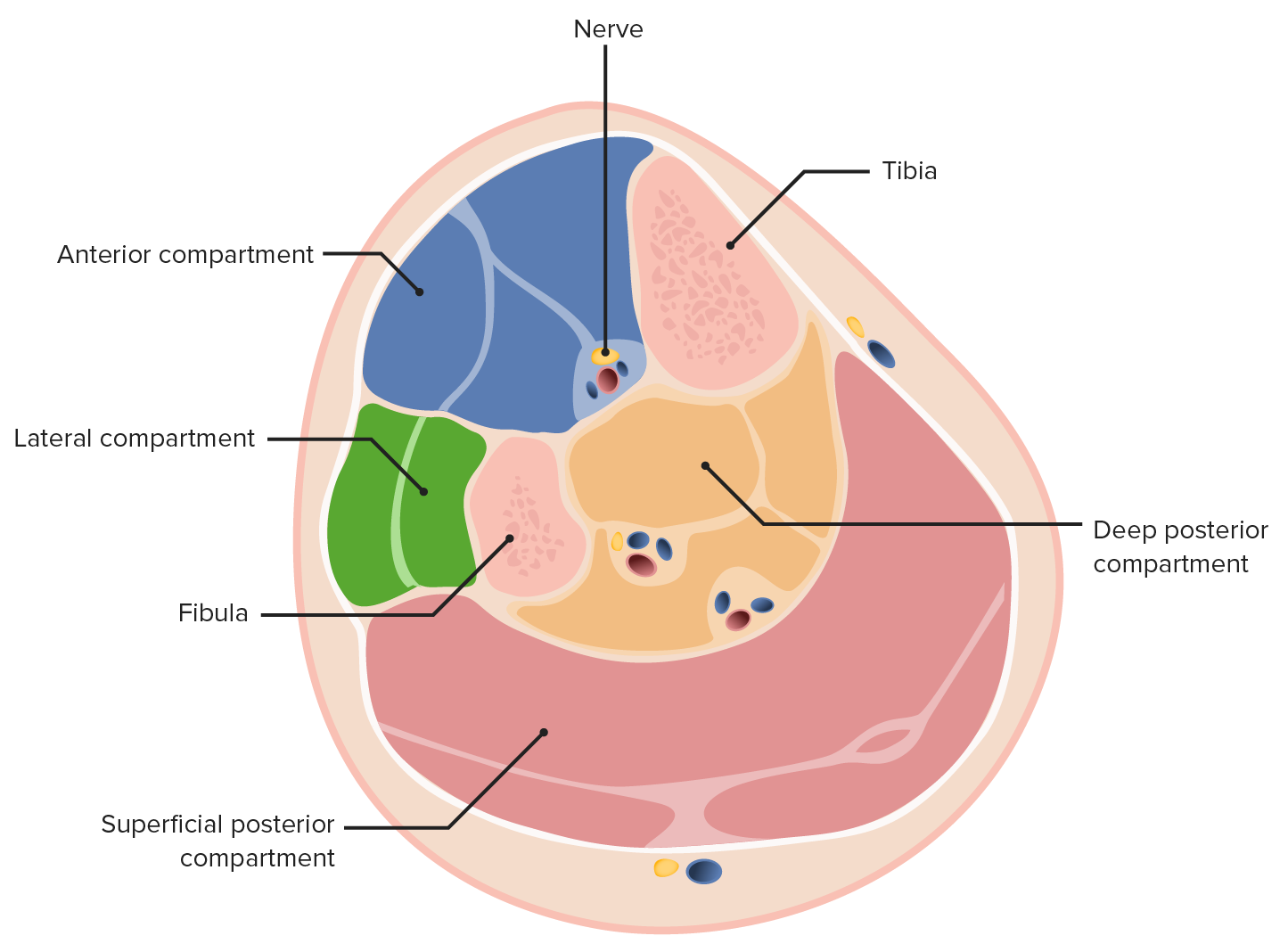
Anterior posterior compartments of leg skin#
perforating branches: pass behind extensor digitorum longus, piercing the deep fascia and supplying the skin of the anterior leg.While still in the posterior compartment of the leg, the anterior tibial artery gives off the: Subsequently, it passes through a gap above the interosseous membrane into the anterior compartment of the leg. anterior tibial recurrent artery: arises immediately, passes upward in the tibialis anterior muscle to anastomose with lateral genicular branches (of the popliteal artery) at the knee The popliteal artery usually divides at the distal border of the popliteus muscle into the tibioperoneal trunk and anterior tibial artery.The anterior tibial artery passes in front of the ankle joint and continues as the dorsalis pedis artery onto the dorsum of the foot lateral to the tendon of the extensor hallucis longus and medial to the extensor digitorum longus and deep peroneal nerve. Here it lies on the interosseous membrane, lateral to tibialis anterior muscle. Subsequently, it passes through a gap above the interosseous membrane into the anterior compartment of the leg.
While still in the posterior compartment of the leg, the anterior tibial artery gives off the: The popliteal artery usually divides at the distal border of the popliteus muscle into the tibioperoneal trunk and anterior tibial artery. The anterior tibial artery arises from the popliteal artery in the popliteal fossa and continues distally as the dorsalis pedis artery.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
